An erection (clinically: penile erection or penile tumescence) is a physiological phenomenon in which the penis becomes firmer, engorged and enlarged.
Anatomy and Physiology of the Breast. The breast is an organ which whose structure reflects its special function: the production of milk for lactation.
Human penis size is described by length and circumference of penis. It is larger than in any other primate. The size depends on arousal level, time of day, room
Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology of the Bull Jack C. Whittier Department of Sciences. Good reproductive performance of a bull is necessary to obtain a high

Found only in men, the prostate is a walnut-sized gland that grows throughout a man’s life and may eventually interfere with or prevent urination by blocking the




Assuming that you have already developed your basic riding skills and abilities to achieve minimum club-riding performance, I recommend the following types of



Human Anatomy and Physiology Questions including “How old is a Stevens Model 94 20 gauge with a plastic stock and the markings 94B and 17 in a circle on the right

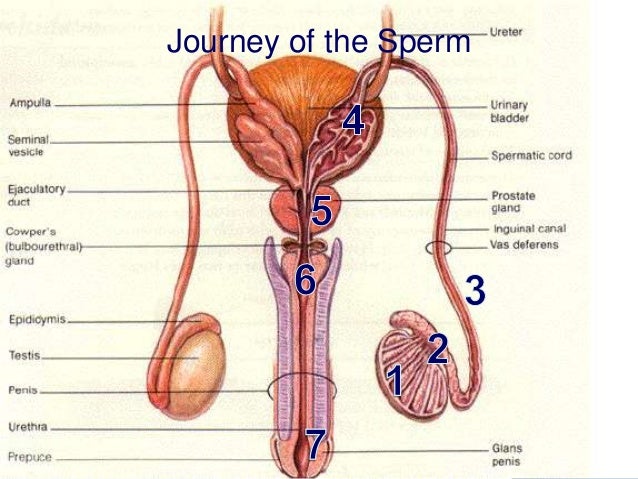
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE INTACT PENIS Contains diagrams and photographs of penile anatomy for educational purposes only.
A penis (plural penises or penes /-n iː z /) is the primary sexual organ that male s use to inseminate sexually receptive mates (usually females and
Tests for erection problems help determine a specific cause for a man’s inability to achieve or maintain an erection (erectile dysfunction or impotence).
You must be logged in to post a comment.